Dam101_unit1
Unit 1: Introduction to Neutral Networks and Deep Learning.
What is AI?
Ability of a machine to imitate human behavior. AI aims to simulate human-like intelligence in machines, enabling them to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and solve complex problems across various domains. It came to existence in 1957 when Arthur Samuel developed a program to play checkers against. And then diversified into text, numbers, speech and images.
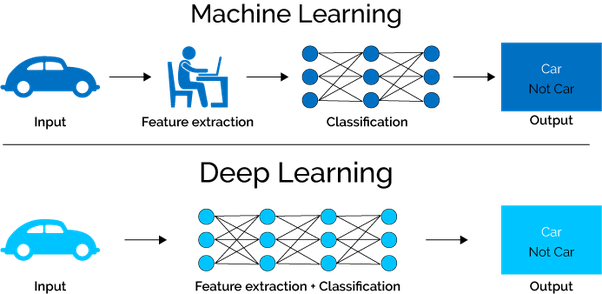
AI techniques include machine learning, where algorithms learn from data and allow software to improve, as well as deep learning, which involves training neural networks to perform specific tasks.
Deep learning is that it is a type of AI that tries to imitate the way the human brain works to solve a problem. It uses its own neural network, to adapt with little to no human intervention. Instead of being definitely programmed to perform a task, deep learning systems learn from examples. It can recognise complex patterns in pictures, text, sounds, and other data to produce accurate predictions.
Importance of Data in AI.
Data serves as a foundation for training, evaluating, and deploying AI models:
- Training AI Models
- Feature Extraction
- Generalisation
- Bias and Fairness
- Validation and Evaluation
- Continuous Learning
- Real-World Applications
Data is the lifeblood of AI learning as it provides the raw material from which AI models derive knowledge and intelligence. Access to high-quality, diverse, and representative data is essential for the development and deployment of effective and moral AI systems.
Neural Network in AI.
Firstly, what is Neuron in Deep Learning?
It is a fundamental building block of neural networks which is also known as perceptron. 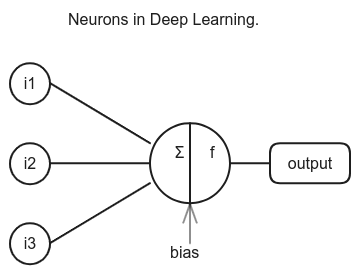
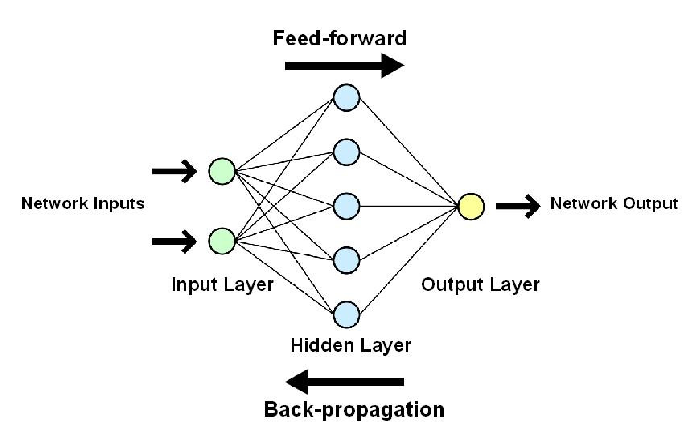
Artificial neurons has three layers; input layer, initial layer where data is introduced to the network. Hidden layer, analyzes the data and the output layer, gives the result.
Now, what is a Neural Network?
Neural networks is basically a method in AI whose function is the same as the human brain. It receives input signals, processes them using weighted connections and produces output signals.
Deep neural networks have several hidden layers linked together. How do they work?
They work by passing input data through multiple layers of interconnected neurons, where each layer performs operations on the data to gradually learn complex representations and patterns.
For example, if the input layer has 3 nodes and the next hidden layer has 4 nodes, then each node on the first layer is connected to all 4 nodes, applies weight , sums them up, and passes the result through an activation function, on the next layer for a total of 12 (3×4) connections. During training, the network’s output is compared to the actual target values using a loss function, which measures the difference between the predicted and true values. Once the loss is calculated, the gradients of the loss function with respect to the weights and biases are summed up using feedback. These are then used to update the weights and biases in the network, iteratively improving its performance.
There are two types of neural networks that are feedforward neural networks that process data in one direction and feedback neural networks where connections between units form a directed cycle.
Supervised and Unsupervised Learning.
Supervised learning and unsupervised learning are two primary categories of machine learning algorithms, distinguished by the type of data.
- Supervised Learning
- In supervised learning, the algorithm learns from labeled data, where each example in the training dataset is paired with a corresponding target or output label.
- Unsupervised Learning
- In unsupervised learning, the algorithm learns from unlabeled data, where the training dataset consists only of input features without corresponding output labels.
- Needs more computational resources.
- No explicit correct answers or labels to guide the learning process.