Dam101_unit2
Unit 2: Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing is the determining step in data analysis, involving cleaning, transforming, and organizing raw data into a format suitable for analysis.
It includes tasks such as removing duplicates, handling missing values, scaling or normalizing features, encoding categorical variables, and splitting the data into training and testing sets. Their goal is to ensure that the data is accurate, complete and prepare raw data in a way that maximizes the performance and effectiveness of data analysis or machine learning algorithms.
Text preprocessing.
Text data is considered as discrete data. Whereby, each word, character, or token represents a discrete unit of data. While text data may involve sequences of words or characters, each individual word or character is considered a discrete entity.
Text preprocessing is an essential step in natural language processing (NLP) that involves cleaning and transforming unstructured text data to prepare it for analysis.
Some of the common operations in data preprocessing includes:
Tokenization: breaking up a given text into units called tokens. It can be done at different levels.
Lowercasing: converting all text to lowercase to ensure consistency and simplify analysis, as uppercase and lowercase versions of words are treated as different entities by most algorithms.
Removing Punctuation: removing punctuations from text data, as they carry semantic meaning and can interfere with analysis. Stopword Removal: Filtering out common words that occur frequently but typically carry little semantic value in text analysis.
- Lemmatization or Stemming: Reducing words to their base or root form to standardize variations of words and improve analysis accuracy. Lemmatization produces valid words, whereas stemming results in non-words.
- Lemmatization: lemmatization reduces the word-forms to the dictionary forms.
- Stemming: reduces derived word forms to stems.
- Handling Contractions and Abbreviations: abbreviations to their full forms to ensure consistency and improve interpretability.
Removing HTML Tags and URLs: removes HTML tags and hyperlinks from text data, which are common in web-based text that does not provide meaningful information for analysis.
Normalization: regulating text data by converting accented characters to their ASCII equivalents, expanding abbreviations, or normalizing spellings to improve consistency.
- Vectorization: Converting text data into numerical representations which is suitable for machine learning algorithms.
Some of the python libraries used for data preprocessing are:
-Pandas
-Numpy
-Scikit-learn
Image preprocessing.
Firstly What is Image?
An image is a binary representation of visual data.It is stored in the form of pixels. Each pixel represents a tiny unit of the image and contains information about its color or intensity. Pixel are often represented using combinations of red, green and blue (RGB). The grid of pixels collectively forms the image that we perceive visually.
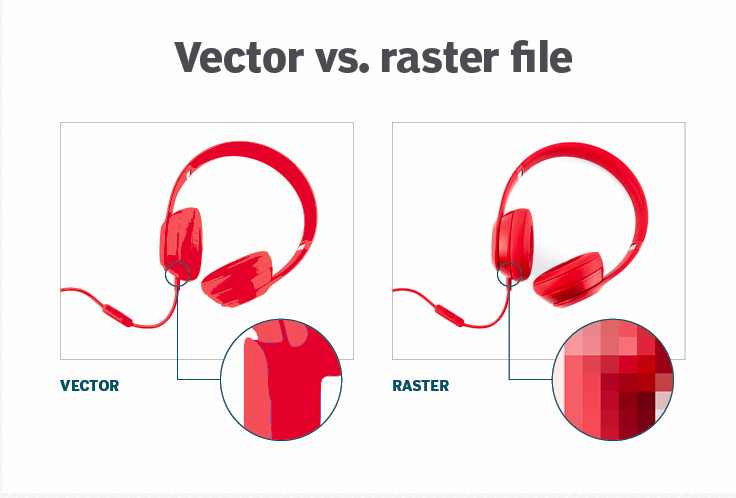
An image can described in terms of vector graphics or raster graphics.
Vector graphics are digital art that is rendered by a computer using a mathematical formula. Raster images are made up of tiny pixels, making them resolution dependent and best used for creating photos.
When deciding between raster vs vector models, one of the primary things to consider is whether the data you are representing is continuous or discrete.
- In general, discrete data is best handled by vector models.
- While continuous data is best left to raster models.
Image File Formats.
The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed.If the data is compressed, it may be done using lossy compression or lossless compression.
Why would I compress images?
Compressed images load faster than uncompressed images. This matters because the speed at which webpages and applications load has a huge impact on conversion rates, the user’s digital experience, and other crucial metrics.
There are two types of image file compression algorithms: lossless and lossy.
Lossless compression algorithms reduce file size while preserving a perfect copy of the original uncompressed image.Lossless compression should be used to avoid accumulating stages of re-compression when editing images.
Lossy compression algorithms preserve a representation of the original uncompressed image that may appear to be a perfect copy, but is not a perfect copy.
The size of raster image files is positively correlated with the number of pixels in the image and the color depth (bits per pixel).
Jpeg
Joint Photographic Experts Group
Nearly every digital camera can save images in the JPEG format, which supports eight-bit grayscale images and 24-bit color images.JPEG applies lossy compression to images, which can result in a significant reduction of the file size.
PNG
Portable Network Graphics
The PNG file format supports 8-bit (256 colors) paletted images and 24-bit truecolor (16 million colors) or 48-bit truecolor with and without alpha channel.
Compared to JPEG, PNG excels when the image has large, uniformly colored areas.
SVG
Scalable Vector Graphics.
SVG defines vector-based graphics in XML format.SVG graphics are scalable, and do not lose any quality if they are zoomed or resized.SVG is supported by all major browsers.
Refers to formats used to describe the layout of a printed page containing text, objects and images.
A PDF file is a combination of vector graphics, text, and bitmap graphics.
Image preprocessing
Image preprocessing means preparing pictures before a computer tries to understand them. It’s like making sure the pictures are in a format that the computer can easily work with.