Dam101_unit3
Unit 3: Convolutional Neural Network
A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a type of artificial neural network used primarily for image recognition and processing, due to its ability to recognize patterns in images. It is widely used for tasks like image recognition, object detection, and facial recognition.
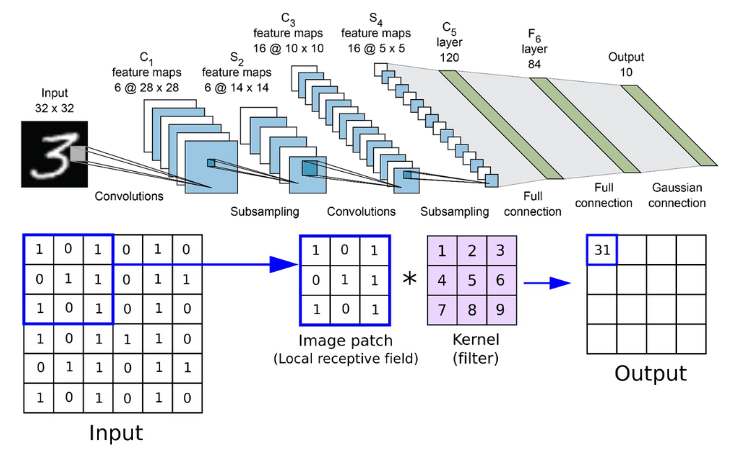
In the context of CNN, convolution is a mathematical operation that combines two functions to produce a third function expressing how the shape of one is modified by the other. This operation is performed by applying a set of weights, known as a filter or kernel, to the input data. The filter slides across the input data, performing a dot product between the filter values and the corresponding input values to produce a feature map.
This process highlights the presence and location of specific features within the input data.
The convolution operation in CNNs is designed to capture local dependencies in the input data, which is particularly useful for image processing where spatial relationships matter. By sliding the filter across the input data, the network can detect features regardless of their position in the image, achieving a form of translation invariance. This means the network can recognize features even if they appear in different positions or orientations within the image.
In summary, convolution in CNNs is a powerful mechanism for extracting and learning features from input data, enabling the network to perform complex tasks such as image classification, object detection, and more.
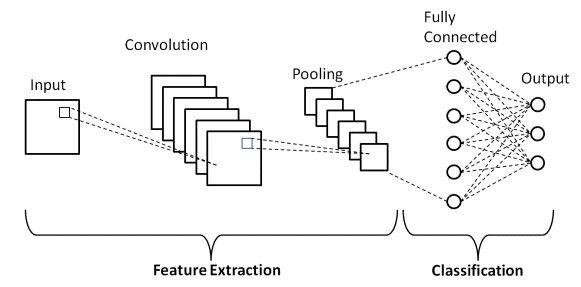
CNNs are structured with several types of layers, including:
Convolutional layers: Where the primary computation happens. Filters are applied to the input data to extract features.
Pooling layers: Reduce the spatial dimensions of the input volume, decreasing computational complexity and reducing overfitting.
Fully connected layers: Perform the final classification or regression task after the feature maps have been extracted and processed through the preceding layers.
The core component of a CNN is the convolutional layer, which applies filters to the input data to extract features. This is the layer where CNNs automatically learn and identify patterns within the data, making them highly effective for tasks that involve recognizing complex structures within images or videos.
Kernals
A filter, or kernel, in a CNN is a small matrix of weights that slides over the input data such as an image. It performs element-wise multiplication with the part of the input it is currently on, and then sums up all the results into a single output pixel.
Types of Kernels:
Size:
Kernels come in various sizes, with common dimensions being 3x3, 5x5, and 7x7. The choice of kernel size affects the level of detail captured and computational efficiency. Larger kernels capture more detailed information but require more computational resources, whereas smaller kernels are quicker but they may miss finer details.
Different kernels can be applied in Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for various effects on an image:
Sharpen Kernel: Enhances edges and details, useful for clarity in tasks like image recognition.
Left and Right Sobel Kernels: Detect vertical edges, aiding in tasks such as object detection.
Gaussian Blur Kernel: Reduces noise and smoothens images, commonly used before processing for tasks like image classification.
The following elements are interconnected in how they affect the size and depth of feature maps in CNNs:
Input Channels: This refers to the number of channels in the input data. In the context of images, it’s usually three for RGB images (red, green, and blue channels).
Feature Maps: Feature maps are the output of applying filters (kernels) to the input data. Each filter produces one feature map. The number of feature maps corresponds to the number of filters used in a convolutional layer.
Number of Kernels: This refers to the number of filters used in a convolutional layer. Each filter is convolved with the input to produce a feature map. The number of kernels determines the depth of the output volume.
Stride: Stride determines how much the filter (kernel) moves across the input data. A larger stride means the filter skips over more pixels at each step, resulting in a smaller output size.
Padding: Padding is adding extra pixels around the input data. It’s often used to preserve the spatial dimensions of the input when applying convolution operations. Padding helps in preventing information loss at the edges of the image.
Depth: Depth refers to the number of feature maps produced by a convolutional layer. It’s determined by the number of kernels used in that layer.
Pooling
Pooling is a fundamental operation in CNNs used to reduce the spatial dimensions of feature maps. It helps in controlling overfitting and reducing computational complexity.
The one value that represents the kernel defines the kind of pooling:
Max Pooling: Selects the maximum value from each window of the input.
Min Pooling: Selects the minimum value from each window of the input.
Average Pooling: Calculates the average value from each window of the input.
Equations that describes how the dimension of an image is altered after convolution and pooling.
Where,
W = width of the image.
H = height of the image.
D = number of channels
K = size of the kernel used
S = stride
P = padding added to the input image.
F = size of the pooling window.
## ##
Object Detection.
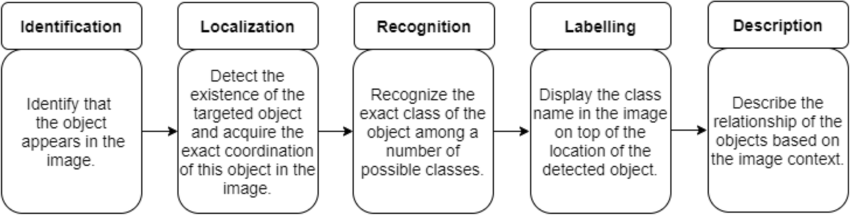
Object detection is a computer vision technique used to identify and locate objects within an image or video. It involves processing an image and determining the presence, location, and the class of objects within it.
The process typically involves several steps:
Input Image: The image or video frame containing objects of interest.
Feature Extraction: This step involves extracting features from the input image that can be used to distinguish between different objects.
Object Localization: Object localization determines the location of objects within the image. This is often achieved by dividing the image into a grid of cells and predicting bounding boxes that tightly enclose the objects.
Object Classification: Once objects are localized, they are classified into different classes. This is typically done using classification models trained on labeled data.
Post-processing: After classification, post-processing techniques are applied to refine the results.
Advanced Techniques in Object Detection and Segmentation:
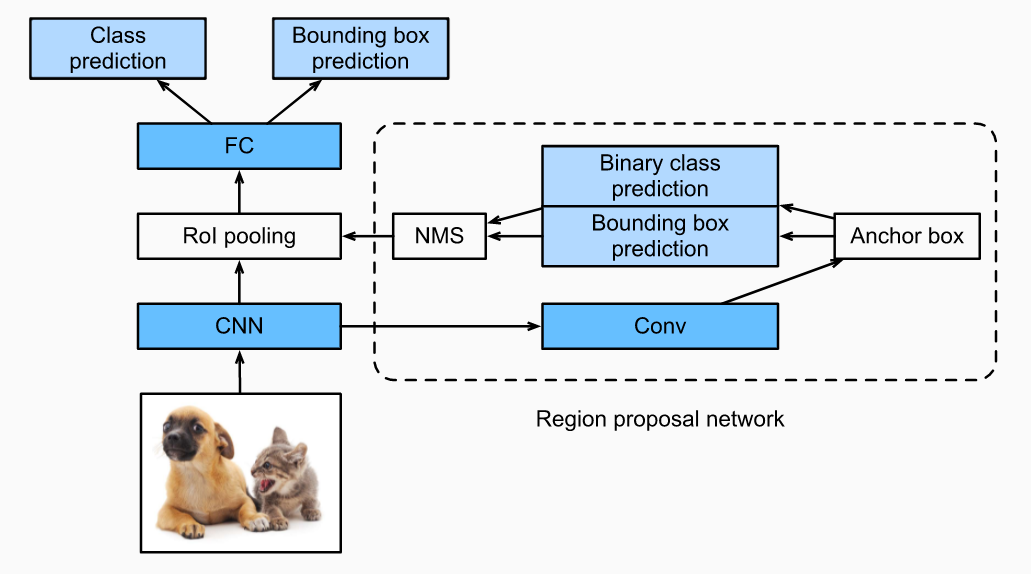
Bounding Box Predictions: Estimating coordinates and dimensions of bounding boxes around objects, often refined using regression models trained on annotated datasets.
Convolutional Implementation of Sliding Windows: Optimizing object detection by efficiently scanning images at multiple scales using convolutional neural networks, eliminating the need for exhaustive search and improving computational efficiency.
Intersection Over Union (IoU): A metric for evaluating the accuracy of object detection algorithms by measuring the overlap between predicted bounding boxes and ground truth annotations.
Non-max Suppression: A post-processing technique used to eliminate redundant or overlapping bounding box predictions by selecting the bounding box with the highest confidence score among overlapping detections.
Anchor Boxes: Predefined bounding boxes of varying aspect ratios and scales used in object detection algorithms like Faster R-CNN and YOLO, serving as reference points during object localization.
Transpose Convolutions: Used in architectures like U-Net for pixel-wise classification tasks, increasing the spatial resolution of feature maps for precise localization of objects.
Convolutional Implementation of Sliding Windows: The sliding windows technique is a fundamental method in computer vision used for object detection and localization within images. It involves systematically scanning an image with a fixed-size window at various positions and scales to detect objects of interest.
There are several popular object detection algorithms, including:
- Single Shot Multibox Detector (SSD)
- Faster R-CNN (Region-based Convolutional Neural Network)
- YOLO (You Only Look Once)
- Mask R-CNN
Special Applications
Face Recognition
Face recognition involves identifying or verifying a person from a digital image or video frame. It’s widely used in security systems, access control, law enforcement, and social media applications. These models can learn discriminative features from facial images and use them to classify or identify individuals.
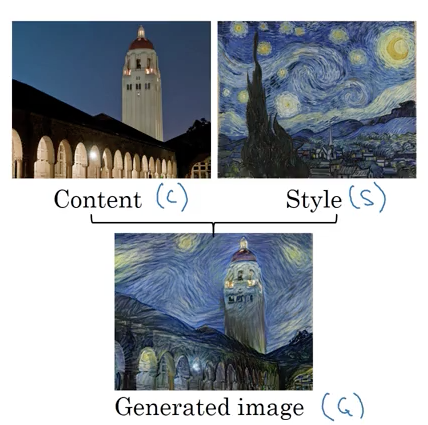
Neural Style Transfer
Neural style transfer, is a technique that allows the style of one image to be applied to another image while preserving the content of the original. This technology combines deep neural networks with optimization algorithms to create visually appealing images with the content of one image and the style of another. It has numerous creative applications, such as generating artwork, transforming photographs into artistic styles, and even creating personalized filters for images and videos.