Dam101_unit4
Unit 4: Hyperparameter Tuning, Regularisation and Optimization
Hyperparameter Tuning
When training machine learning models, each dataset and model needs a different set of hyperparameters, which are a kind of variable. The only way to determine these is through multiple experiments, where we pick a set of hyperparameters and run them through the model. This is called hyperparameter tuning.
Hyperparameters in Neural Networks
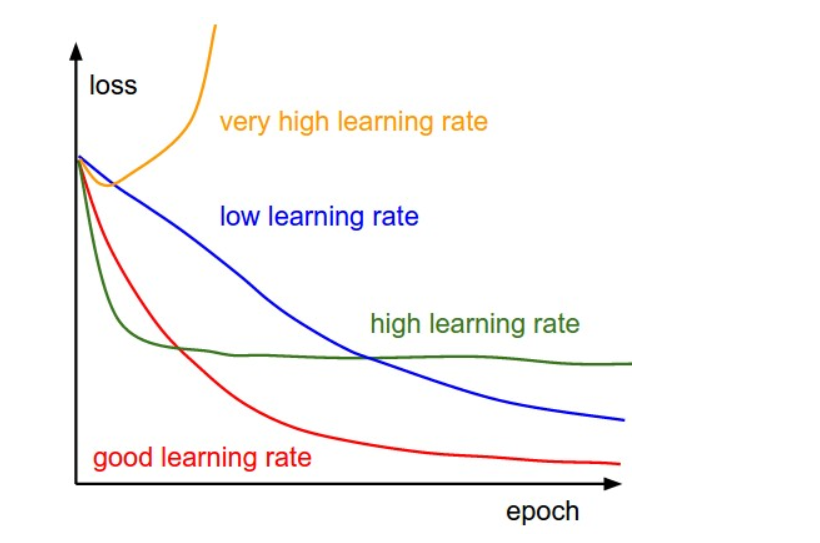
Learning rate: Controls the step size taken by the optimizer during each iteration of training.
Epochs: Represents the number of times the entire training dataset is passed through the model during training.
Number of layers: Determines the depth of the model, which can have a significant impact on its complexity and learning ability.
Number of nodes per layer: Determines the width of the model, influencing its capacity to represent complex relationships in the data.
Architecture: Determines the overall structure of the neural network, including the number of layers, the number of neurons per layer, and the connections between layers.
Activation function: This hyperparameter introduces non-linearity into the model, allowing it to learn complex decision boundaries. eg. sigmoid, tanh, and Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU).
Hyperparameter Tuning techniques
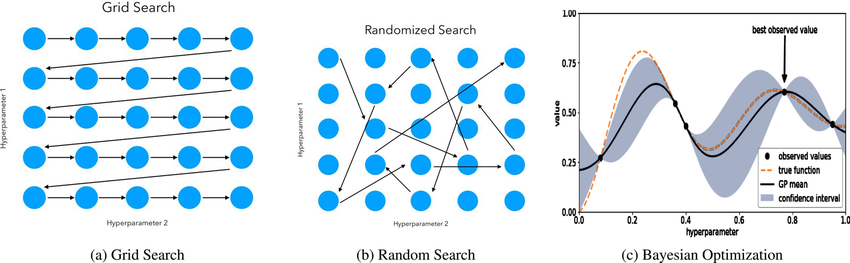
Grid Search: In grid search, we define a grid of hyperparameter values to search. The algorithm then evaluates the model performance for each combination of hyperparameters specified in the grid which allows us to find the optimal set of hyperparameters.
Random Search: Random search selects hyperparameter values randomly from predefined ranges. This approach is often more efficient than grid search because it explores a broader range of hyperparameter values.
Bayesian Optimization: Bayesian optimization uses probabilistic models to model the objective function and decides where to sample the next set of hyperparameters based on the previous evaluations.
- This method is particularly useful when the search space is large and expensive to evaluate.
Applications of Hyperparameter Tuning:
Model Selection: Choosing the Right Model Architecture for the Task
- Regularization Parameter Tuning: Controlling Model Complexity for Optimal Performance
- Feature Preprocessing Optimization: Enhancing Data Quality and Model Performance
- Algorithmic Parameter Tuning: Adjusting Algorithm-Specific Parameters for Optimal Results
##
Regulisation and Optimization
Regulisation
Regularization is a technique used to address overfitting by directly changing the architecture of the model by modifying the model’s training process.
These are the commonly used regularization techniques:
- L2 regularization
- L1 regularization
- Dropout regularization
Optimization
Optimization refers to the process of adjusting the parameters of a model to minimize or maximize a certain objective function.It typically involves finding the set of model parameters that minimizes a predefined loss function. Optimization algorithms are used to iteratively update the model parameters based on the gradients of the loss function with respect to the parameters.
Gradient Descent is the widely used optimization algorithm that iteratively moves towards the minimum of the loss function by taking steps proportional to the negative of the gradient.
Variants of Gradient Descent have been developed to improve convergence speed and performance such as such as Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), Mini-batch Gradient Descent, and Adam.
.png)