Dbs101_flippedclass12
Topic : Recovery Systems and Algorithm in DBMS
What is Recovery Systems in DBMS?
Recovery systems in DBMS refer to the set of mechanisms, techniques, and procedures put in place to address failures and restore databases to a consistent and reliable state after unexpected events such as system crashes, power outages, or hardware failures.
Database recovery techniques like ARIES and Fuzzy Checkpoints are crucial for maintaining the integrity and availability of data within database management systems.
Algorithms for Recovery and Isolation Exploiting Semantics (ARIES)
It’s a well-known algorithm used for database recovery after a system crash or failure.
Main principles behind ARIES:
Write-Ahead Logging (WAL): Changes are logged before they’re written to the database, ensuring durability.
Repeating History during Redo: After a crash, ARIES replays logged actions to restore the exact pre-crash state, then applies committed transactions’ changes.
Logging Changes during Undo: Undoing transactions is logged to prevent repeated actions during recovery, maintaining database integrity.
Logging
In ARIES, logging is crucial for database recovery.
All operations are logged with increasing Sequence Numbers, stored safely. The dirty page table tracks modified pages awaiting disk write, and the transaction table manages active transactions.
Log records include details like Sequence Number, Transaction ID, Page ID, Redo, and Undo information. Transactions start with “Update” and end with “End Of Log” (EOL). Compensation Log Records (CLRs) mark actions already undone during recovery or aborted transaction undo. CLRs contain essential details excluding Undo.
This logging system ensures reliable recovery and efficient transaction management.
Recovery
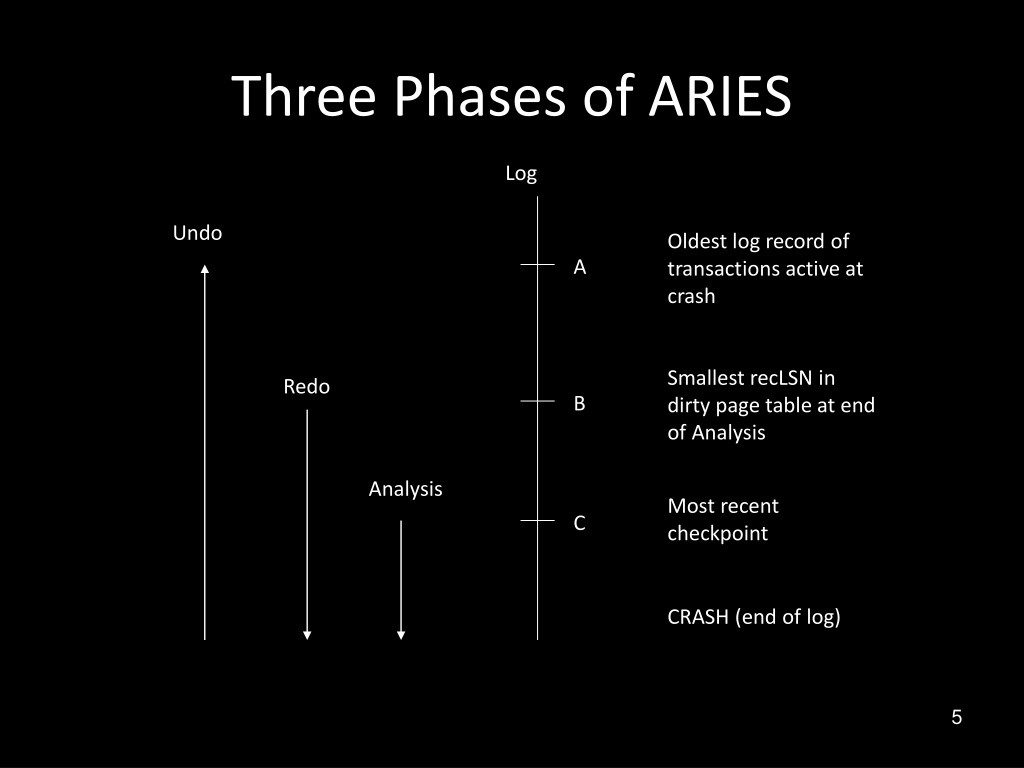
The ARIES recovery algorithm consists of three main phases: Analysis, Redo, and Undo.
These phases ensure that the database can be restored to a consistent state after a crash, even if the crash occurs during the recovery process itself.
Analysis Phase:
During this phase, ARIES analyzes the contents of the transaction log to determine the state of transactions and database pages at the time of the crash.
Analysis Phase: ARIES examines log to assess transaction and page states.
Reconstruction: Rebuilds transaction table, dirty page table, and log sequence numbers.
Checkpoint Reference: Starts analysis from recent checkpoint, reads log forward to rebuild state.
Redo Phase:
In the Redo phase, ARIES ensures that all updates made by committed transactions are reapplied to the database.
Redo Phase: ARIES scans log forward from Analysis start.
Apply Changes: Reapplies committed transaction updates to dirty pages post-checkpoint.
Consistent State: Ensures database matches state at crash, with all committed changes re-executed.
Undo Phase:
The Undo phase of ARIES ensures that changes made by transactions that were active at the time of the crash but not committed are undone.
Undo Phase: ARIES scans the log backward to find incomplete transactions.
- Rollback: It undoes changes made by incomplete transactions to ensure a consistent state.
- Compensation Log Records: ARIES writes CLRs to enable crash recovery during the recovery process.
Checkpoints
Checkpoints optimize database recovery by reducing log scanning overhead. They offer a snapshot of the database state, including the Dirty Page Table (DPT) and Transaction Table (TT), for efficient recovery after a crash.
Fuzzy logging, is a technique used to create checkpoints without having to lock the entire database, thereby minimizing disruptions to ongoing transactions.
Process in fuzzy logging;
Logging Transactions: Continuously log all database changes.
Insert Marker: Periodically insert a “Fuzzy Log Starts Here” marker.
Record Checkpoint Data: Following the marker, record snapshot of DPT and TT.
- Recovery: During recovery, locate marker and corresponding checkpoint data.
Restore State: Restore DPT and TT from checkpoint data.
- Resume Processing: Resume transaction processing from consistent state, reducing recovery time.
Overall, fuzzy logging and checkpointing are essential techniques in database recovery, providing a balance between ensuring data consistency and minimizing performance overhead.
Conclusion
ARIES stands as a robust and efficient recovery mechanism in database management systems. Through its meticulous logging, analysis, redo, and undo phases, ARIES ensures data integrity and consistency, even in the face of system failures or crashes. By leveraging techniques like checkpoints and compensation log records, ARIES minimizes recovery time and overhead, making it a cornerstone for reliable and efficient database recovery. Its versatility and effectiveness make it a vital component in modern database systems, providing peace of mind for both users and administrators alike.
.jpg)