Dbs101_flippedclass5
Topic : Normal Forms
First, what is normalization?
Normalization is the process of organizing a database to minimize redundancy and dependency by dividing large tables into smaller tables and defining relationships between them. This helps to ensure that the design of a database is efficient, organized, and free from data anomalies. There are several levels of normalization, each with its own set of guidelines, known as normal forms.
Therefore, Normal Forms in SQL basically refers to a set of guidelines for organizing relational databases to minimize redundancy and dependency.
These are the normal forms we discussed in the class:
- First Normal Form (1NF)
In 1NF, each table cell should contain only a single valueed attributes, and each column should have a unique name. The first normal form helps to eliminate duplicate data and simplify queries.
Here is an example I found in Google:
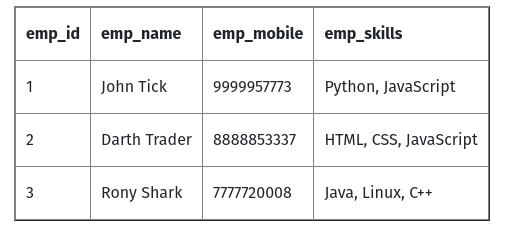
This is unnormalized table:
- emp_skills column holds multiple comma-separated values, therefore it fails to pass 1NF.
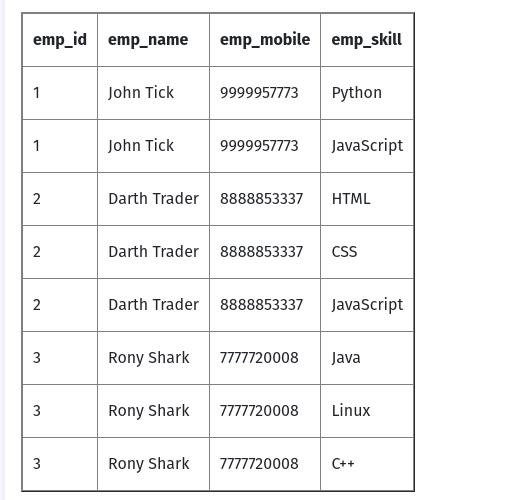
This is how they fixed the table.
- added multiple rows to add multiple skills so each column have a single value.
- Second Normal Form (2NF)
2NF requires that the table is in 1NF and that all non-key attributes are fully functional dependent on the primary key and eliminates partial dependencies.
Example:
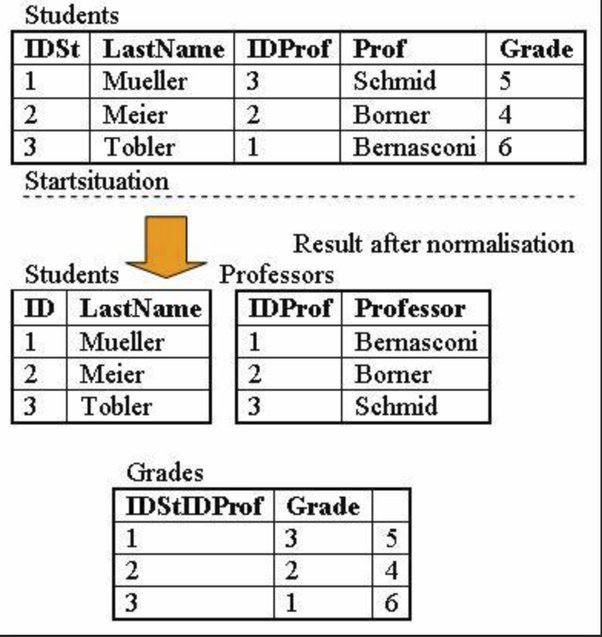
This is table called ‘students’ with the primary_keys (‘IDSTD,IDPROF’) that forms the composite primary key because each combination uniquely identifies a row in the table.
However, the column Grade don’t dependent on the entire primary key (Order_ID, Product_ID). It is only dependent on ‘IDPROF’.
-To normalize this table into 2NF, we split it into two tables.
- Third Normal Form (3NF)
Builds on 2NF and requires that there are no transitive dependencies. This means that each column should be directly related to the primary key, and not to any other columns in the same table.
- Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF)
A precise form of 3NF that ensures that each non-key attribute is dependent only on the candidate key and eliminates certain types of anomalies related to functional dependencies.
- Fourth Normal Form (4NF)
Ensures that a table does not contain any multi-valued dependencies. The basic condition with Fourth Normal Form is that the relation must be in BCNF.
This helps in reducing redundancy, improving data integrity, and making the database more efficient and also increases consistency. And It is important to strike a balance between normalization and practicality when designing a database because higher levels of normalization can lead to more complex database designs and queries.
During this flipped class, same like the classes before we formed groups on the 4 subtopics under Normal Forms and presented them to the class. Also, we presented demos on some of the databases we used for conveying more information and for better understanding.