Dbs101_flippedclass9
Topic : Query Optimization
In todays flipped class, we conducted a quiz based on the topic Query Optimization.
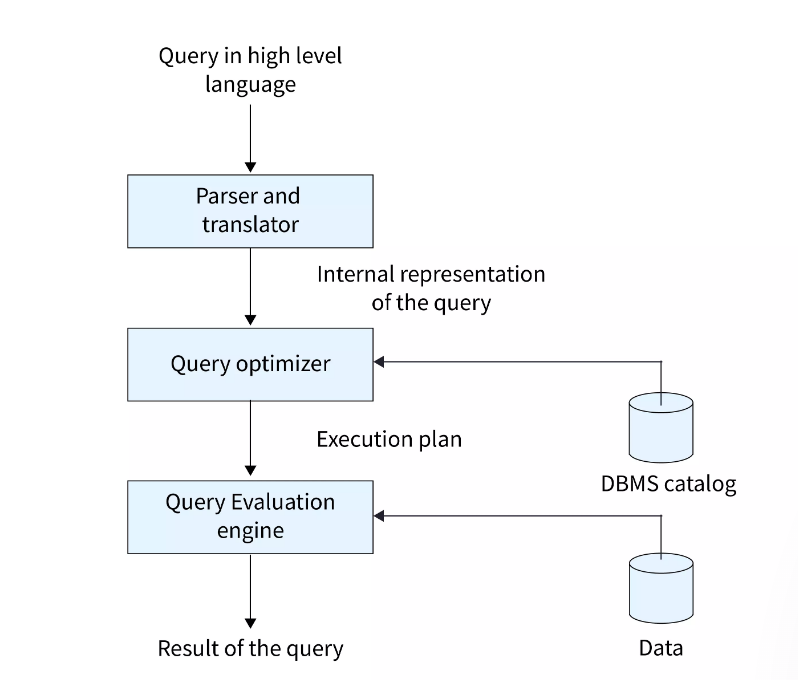
First of all, What is a Query Optimization?
Query Optimization is a crucial aspect of database management systems (DBMS) that seeks to determine the most efficient way to execute a given query by considering a variety of query execution strategies.
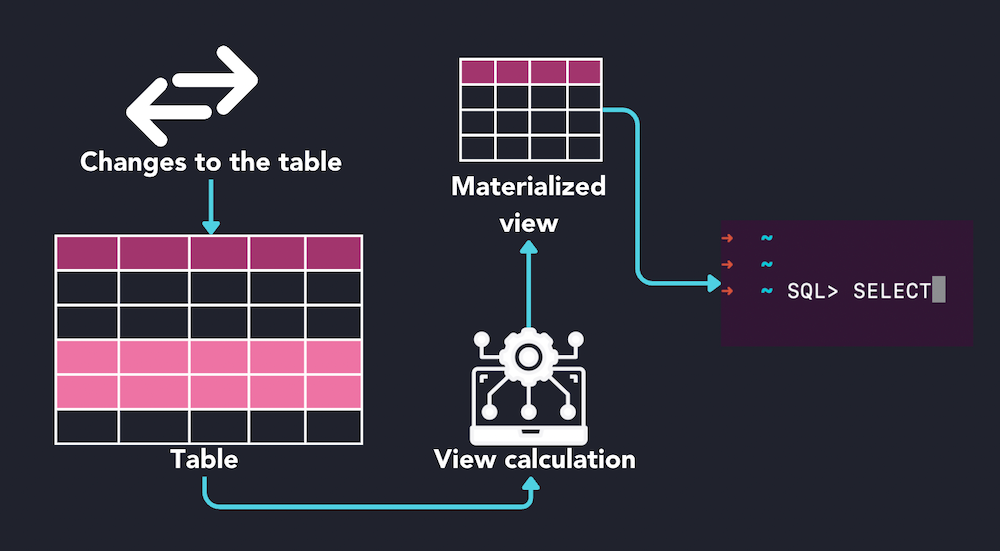
Materialized View
A materialized view is a database object that stores the result of a query physically, similar to a table. Unlike a regular view, which is a virtual table based on the result-set of an SQL statement, a materialized view contains the actual data stored in the database. This means that once the materialized view is created, it holds the data until it is refreshed manually or according to a schedule. Materialized views are particularly useful for complex queries that would otherwise take a long time to compute because they store the result set of the query, making subsequent access much faster.
Characteristics of materialized views include:
Performance Improvement: Since the data is pre-computed and stored, accessing the materialized view can be much quicker than running the underlying query again, especially for complex calculations or joins.
Data Refresh: Materialized views need to be refreshed periodically to reflect changes in the underlying data. This can be done manually or scheduled to occur automatically at certain intervals.
Storage Considerations: Because materialized views store data, they consume disk space. The amount of storage needed depends on the size of the result set of the query.
Usage Scenarios: They are commonly used in reporting and analytical applications where the data does not change frequently but needs to be accessed quickly.
Materialized views offer a balance between the flexibility of views and the performance benefits of physical storage, making them a valuable tool in database design for scenarios where query performance is critical.
Advanced Topics in Query Optimization
Advanced topics in query optimization involves sophisticated techniques and strategies designed to enhance the efficiency of database operations beyond basic optimizations. These advanced strategies focus on optimizing specific types of queries and addressing complex framework that can significantly impact database performance. Here are some key advanced topics:
Top-K Optimization
This involves optimizing queries that return only the top K results from a sorted dataset. Methods include using pipelined query evaluation plans to produce results in sorted order and estimating the highest value on sorted attributes to eliminate larger values early in the process. This prevents unnecessary computation and discards extra tuples beyond the top K results.
Join Minimization
Join minimization aims to reduce the number of join operations required to compute a query, especially in scenarios involving views. By identifying and dropping unnecessary relations from joins, this technique can simplify query execution plans and improve performance.
Optimization of Updates
Update queries modify existing data and can be challenging to optimize due to the potential for affecting query execution and causing issues like the “Halloween problem.” Techniques include executing update queries in stages, handling updates during index scans, and batching updates to reduce overhead. Optimizing update queries ensures minimal disruption to query performance and efficient data modification.
Multi-Query Optimization and Shared Scans
This strategy focuses on optimizing batches of queries submitted together. It leverages common subexpressions between queries to compute and reuse results, reducing the overall cost of query evaluation. Shared scans allow multiple queries to scan a relation once, avoiding repeated disk reads and improving efficiency for operations on large datasets.
Parametric Query Optimization
Involves optimizing queries without knowing their exact parameter values upfront. The optimizer generates multiple plans for different parameter values and selects the most cost-effective plan after the parameters are known. This approach allows for dynamic optimization based on runtime conditions, leading to more efficient query execution
These advanced topics for query optimization, aims to address specific challenges and leverage database capabilities to achieve superior performance.